Few things to note
- if you want to prevent directory traversal we need to setup chroot with vsftpd (not covered on this KB)
- For the demo I just used Unencrypted FTP on port 21 to keep things simple, Please utilize SFTP with the letsencrypt certificate for better security. i will cover this on another article and link it here
Update and Install packages we need
sudo dnf update
sudo dnf install net-tools lsof unzip zip tree policycoreutils-python-utils-2.9-20.el8.noarch vsftpd nano setroubleshoot-server -y
Setup Groups and Users and security hardening
if you want to prevent directory traversal we need to setup chroot with vsftpd (not covered on this KB)
Create the Service admin account
sudo useradd ftpadmin
sudo passwd ftpadmin
Create the group
sudo groupadd FTP_Root_RW
Create FTP only user shell for the FTP users
echo -e '#!/bin/sh\necho "This account is limited to FTP access only."' | sudo tee -a /bin/ftponly
sudo chmod a+x /bin/ftponly
echo "/bin/ftponly" | sudo tee -a /etc/shells
Create FTP users
sudo useradd ftpuser01 -m -s /bin/ftponly
sudo useradd ftpuser02 -m -s /bin/ftponly
user passwd ftpuser01
user passwd ftpuser02
Add the users to the group
sudo usermod -a -G FTP_Root_RW ftpuser01
sudo usermod -a -G FTP_Root_RW ftpuser02
sudo usermod -a -G FTP_Root_RW ftpadmin
Disable SSH Access for the FTP users.
Edit sshd_config
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Add the following line to the end of the file
DenyUsers ftpuser01 ftpuser02
Open ports on the VM Firewall
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=20-21/tcp
#Allow the passive Port-Range we will define it later on the vsftpd.conf
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=60000-65535/tcp
#Reload the ruleset
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Setup the Second Disk for FTP DATA
Attach another disk to the VM and reboot if you haven’t done this already
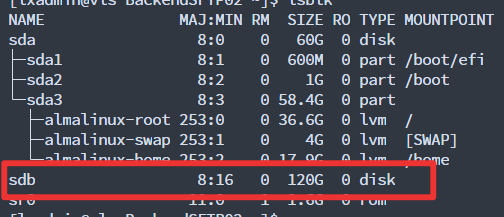
lsblk to check the current disks and partitions detected by the system
lsblk
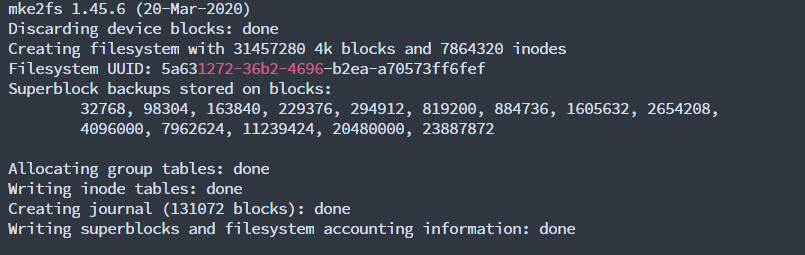
Create the XFS partition
sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb
# use mkfs.ext4 for ext4
Why XFS? https://access.redhat.com/articles/3129891
Create the folder for the mount point
sudo mkdir /FTP_DATA_DISK
Update the etc/fstab file and add the following line
sudo nano etc/fstab
/dev/sdb /FTP_DATA_DISK xfs defaults 1 2
Mount the disk
sudo mount -a
Testing
mount | grep sdb

Setup the VSFTPD Data and Log Folders
Setup the FTP Data folder
sudo mkdir /FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root -p
Create the log directory
sudo mkdir /FTP_DATA_DISK/_logs/ -p
Set permissions
sudo chgrp -R FTP_Root_RW /FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/
sudo chmod 775 -R /FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/
Setup the VSFTPD Config File
Backup the default vsftpd.conf and create a newone
sudo mv /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpdconfback
sudo nano /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
#KB Link - ####
anonymous_enable=NO
local_enable=YES
write_enable=YES
local_umask=002
dirmessage_enable=YES
ftpd_banner=Welcome to multicastbits Secure FTP service.
chroot_local_user=NO
chroot_list_enable=NO
chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
listen=YES
listen_ipv6=NO
userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd/user_list
pam_service_name=vsftpd
userlist_enable=YES
userlist_deny=NO
listen_port=21
connect_from_port_20=YES
local_root=/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/
xferlog_enable=YES
vsftpd_log_file=/FTP_DATA_DISK/_logs/vsftpd.log
log_ftp_protocol=YES
dirlist_enable=YES
download_enable=NO
pasv_enable=Yes
pasv_max_port=65535
pasv_min_port=60000
Add the FTP users to the userlist file
Backup the Original file
sudo mv /etc/vsftpd/user_list /etc/vsftpd/user_listBackup
echo "ftpuser01" | sudo tee -a /etc/vsftpd/user_list
echo "ftpuser02" | sudo tee -a /etc/vsftpd/user_list
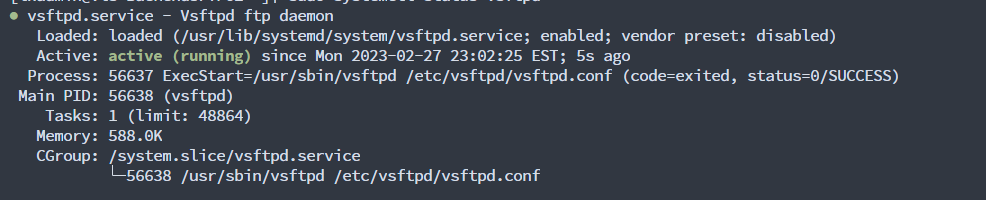
sudo systemctl start vsftpd
sudo systemctl enable vsftpd
sudo systemctl status vsftpd
Setup SELinux
instead of putting our hands up and disabling SElinux, we are going to setup the policies correctly
Find the available policies using getsebool -a | grep ftp
getsebool -a | grep ftp
ftpd_anon_write --> off
ftpd_connect_all_unreserved --> off
ftpd_connect_db --> off
ftpd_full_access --> off
ftpd_use_cifs --> off
ftpd_use_fusefs --> off
ftpd_use_nfs --> off
ftpd_use_passive_mode --> off
httpd_can_connect_ftp --> off
httpd_enable_ftp_server --> off
tftp_anon_write --> off
tftp_home_dir --> off
[lxadmin@vls-BackendSFTP02 _logs]$
[lxadmin@vls-BackendSFTP02 _logs]$
[lxadmin@vls-BackendSFTP02 _logs]$ getsebool -a | grep ftp
ftpd_anon_write --> off
ftpd_connect_all_unreserved --> off
ftpd_connect_db --> off
ftpd_full_access --> off
ftpd_use_cifs --> off
ftpd_use_fusefs --> off
ftpd_use_nfs --> off
ftpd_use_passive_mode --> off
httpd_can_connect_ftp --> off
httpd_enable_ftp_server --> off
tftp_anon_write --> off
tftp_home_dir --> off
Set SELinux boolean values
sudo setsebool -P ftpd_use_passive_mode on
sudo setsebool -P ftpd_use_cifs on
sudo setsebool -P ftpd_full_access 1
"setsebool" is a tool for setting SELinux boolean values, which control various aspects of the SELinux policy.
"-P" specifies that the boolean value should be set permanently, so that it persists across system reboots.
"ftpd_use_passive_mode" is the name of the boolean value that should be set. This boolean value controls whether the vsftpd FTP server should use passive mode for data connections.
"on" specifies that the boolean value should be set to "on", which means that vsftpd should use passive mode for data connections.
Enable ftp_home_dir --> on if you are using chroot
Add a new file context rule to the system.
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t public_content_rw_t "/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/(/.*)?"
"fcontext" is short for "file context", which refers to the security context that is associated with a file or directory.
"-a" specifies that a new file context rule should be added to the system.
"-t" specifies the new file context type that should be assigned to files or directories that match the rule.
"public_content_rw_t" is the name of the new file context type that should be assigned to files or directories that match the rule. In this case, "public_content_rw_t" is a predefined SELinux type that allows read and write access to files and directories in public directories, such as /var/www/html.
"/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/(/.)?" specifies the file path pattern that the rule should match. The pattern includes the "/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/" directory and any subdirectories or files beneath it. The regular expression "/(.)?" matches any file or directory name that may follow the "/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/" directory path.
In summary, this command sets the file context type for all files and directories under the "/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/" directory and its subdirectories to "public_content_rw_t", which allows read and write access to these files and directories.
Reset the SELinux security context for all files and directories under the “/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/”
sudo restorecon -Rvv /FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/
"restorecon" is a tool that resets the SELinux security context for files and directories to their default values.
"-R" specifies that the operation should be recursive, meaning that the security context should be reset for all files and directories under the specified directory.
"-vv" specifies that the command should run in verbose mode, which provides more detailed output about the operation.
"/FTP_DATA_DISK/FTP_Root/" is the path of the directory whose security context should be reset.
Setup Fail2ban
Install fail2ban
sudo dnf install fail2ban
Create the jail.local file
This file is used to overwrite the config blocks in /etc/fail2ban/fail2ban.conf
sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
vsftpd]
enabled = true
port = ftp,ftp-data,ftps,ftps-data
logpath = /FTP_DATA_DISK/_logs/vsftpd.log
maxretry = 5
bantime = 7200
Make sure to update the logpath directive to match the vsftpd log file we defined on the vsftpd.conf file
sudo systemctl start fail2ban
sudo systemctl enable fail2ban
sudo systemctl status fail2ban
journalctl -u fail2ban will help you narrow down any issues with the service
Testing
sudo tail -f /var/log/fail2ban.log
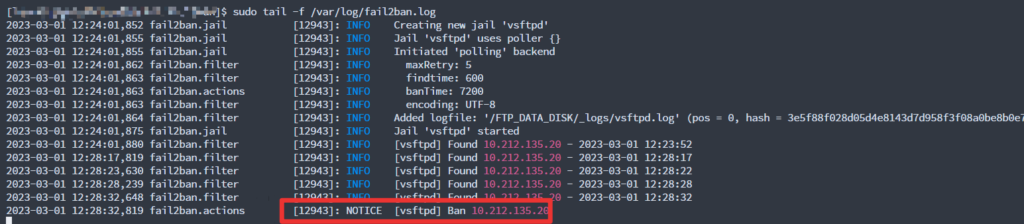
Fail2ban injects and manages the following rich rules

Client will fail to connect using FTP until the ban is lifted
Remove the ban IP list
#get the list of banned IPs
sudo fail2ban-client get vsftpd banned
#Remove a specific IP from the list
sudo fail2ban-client set vsftpd unbanip <IP>
#Remove/Reset all the the banned IP lists
sudo fail2ban-client unban --all
This should get you up and running, For the demo I just used Unencrypted FTP on port 21 to keep things simple, Please utilize SFTP with the letsencrypt certificate for better security. i will cover this on another article and link it here